Key to Order Araneae (spiders)
E. A. Heinrichs
Lincoln, Nebraska
Updated: January 2022
About
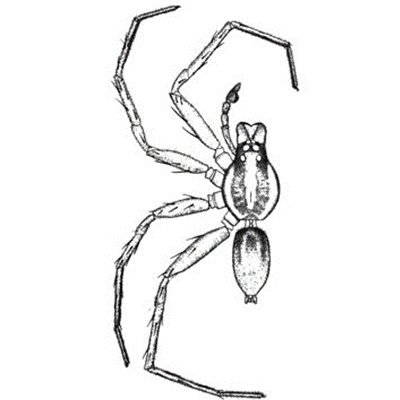
There is an abundance of spider species in the West African rice ecosystems. They serve as a major factor in the biological control of rice insect pests. Adult spiders are commonly found near the base of the rice plant. The hunting spiders (Lycosa) are of major importance and considered the most important predators of rice fields. Hunting spiders actively hunt their prey, especially nymphal and adult leaf-and planthoppers, and do not construct a web. The male hunting spider is distinguished by its large pedipalps (the second pair of appendages in the cephalothorax used to hold down and crush prey). The web spinning Tetragnatha, although present in rice, are not considered important predators or rice pests. Key characters used in the identification of spider species are the fangs of the chelicerae, pedipalps, carapace, claws, eyes, spinnerets, legs and abdomen.